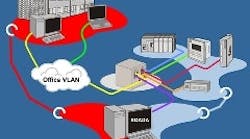
Overtapped VLANs, rate limiting, and port security can help protect control networks from problems with office networks.
Rate limiting is a managed-switch feature that can limit the bandwidth consumed by devices connected to specific ports of the switch. Users can specify a maximum bandwidth for each port of the switch. This can be used, for example, to limit the level of traffic sent to a sensitive piece of equipment. Another use of this feature is to limit traffic sent to the control network from the office network. “In this way excessive traffic problems created by the office network, such as broadcast or directed-message storms, can be controlled by rate limiting,” explains Levine. “It’s recommended that rate limiting be used on all switch ports that connect to any Windows PCs. Rate limiting can also control the level of multicast messages.”
Port security can be used to control which devices can communicate through specific ports of a managed switch. This can determine which office network devices can communicate with the control network. For example, port security can be used to only allow the plant manager and the engineering manager to have access to the control network from their computers on the office network.