Machine Drives Use Half of Sector Electricity
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, machine drives — mostly electric motors, pumps and fans — account for about half of the manufacturing sector's delivered electricity use and 8% of the sector's total fuel consumption. Their wide use across many industries results in a substantial impact on the demand placed on power grids. EIA's Annual Energy Outlook 2013 (AEO2013) projects that the continuing increase in the energy efficiency of machine drives will offset an increase in industrial output, resulting in relatively flat levels of electricity consumption by machine drives.
The level of electricity used in manufacturing or other activities has broader implications for total energy use. It takes three units of primary energy (from fuels such as coal, nuclear and natural gas) to generate one unit of electricity, meaning that increased electricity use has a disproportionate effect on the amount of total primary energy required to support site-level energy use. Reported electricity use is based on energy consumption for end use (delivered energy).
Both fossil fuels and electricity are used to power manufacturing processes. Fossil fuels may be used to drive turbines, reciprocating engines and other prime movers that provide mechanical power for rotating machinery. Electric motors can also be used for the same purposes as well as for pumps, fans and air compressors. In total, electricity powers about 89% of motors in manufacturing. Electric motors are used in a wide variety of materials handling and materials processing operations (e.g., machining).
Power Hungry Motors and Drives
Machine drives and motors gobble up about half of manufacturing's electricity, but EIA reports that coming efficiencies will offset future consumption increases.
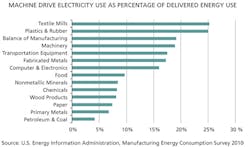
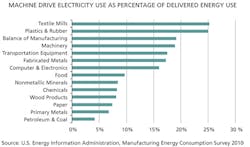
Machine drives account for an average of close to 10% of delivered energy use in manufacturing. In some industries, such as textiles, plastics and rubber, this share can approach 25%. On the other hand, machine drives used in more energy-intensive industries, such as petroleum and coal products, food products and chemicals, tend to account for a smaller share of energy use within that industry because of the significant amounts of energy needed for other parts of the manufacturing process. However, the use of machine drives in energy-intensive manufacturing processes accounts for about 70% of total manufacturing electric motor energy consumption.
The effects of increases in shipments and increases in energy efficiency are considered in EIA's long-term energy projections. For example, in AEO2013, the chemicals industry's electricity use for motors is projected to decline by 14% between 2010 and 2040, along with a 14% increase in shipments. The transportation equipment industry's electricity use for machine drives is projected to increase by 109%, along with a 165% increase in shipments, over that same period. For new motors, the AEO2013 Reference case includes a 0.63% gain in efficiency per year for motors used in the transportation equipment industry and a 0.54% gain in efficiency per year for motors used in the chemicals industry. These projections reflect an analysis of historical efficiency gains as well as current technology and its potential for further efficiency gains.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy's sourcebook for improving motor and drive system performance, electricity costs make up about 96% of the total lifecycle cost of a motor, while capital costs make up 3%, and maintenance makes up 1% to account for the rest. As a result, energy efficiency measures can have a significant effect on the total ownership costs related to machine drives, including the use of optimally sized energy-efficient motors and proper motor maintenance.