Raj Rajendra, product consultant/manager, Distributed IO & Logic Controller, Siemens: IO-Link is a point-to-point network. It connects one device to one port of the IO-Link master that may have several ports.
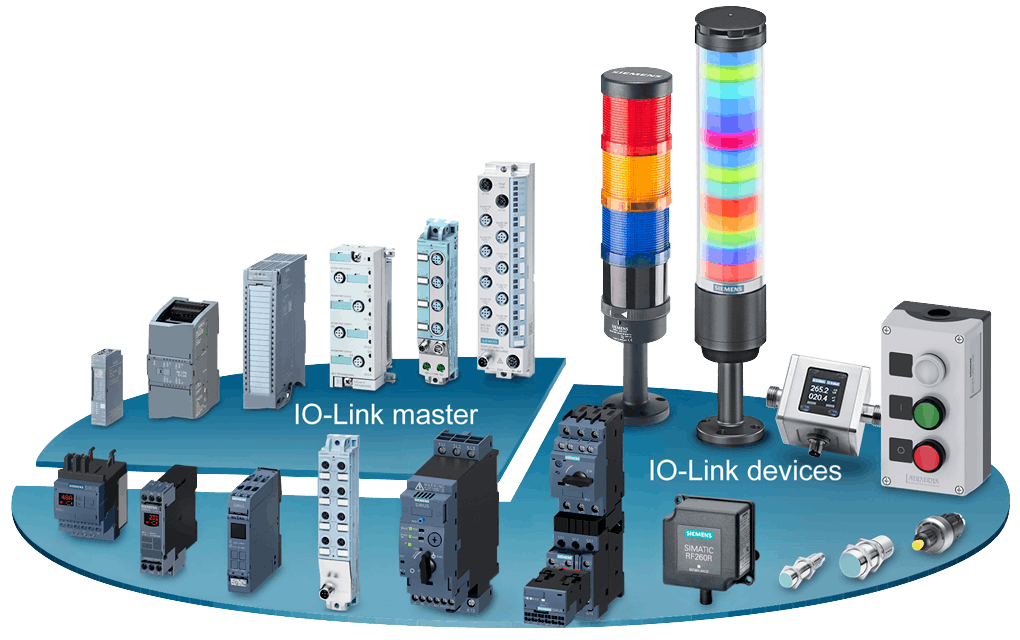
Raj Rajendra, product consultant/manager, Distributed IO & Logic Controller, Siemens: Siemens provides IO-Link masters for all our IO Series, and we also offer devices from our Factory Automation business and other business units of Siemens (Figure 1). The devices include IP65/67-rated IO, motor starters, relays, RFID tag readers, LED signal columns, switch boxes, power supplies and more. Our IO-Link master modules are MultiFieldbus (MFB) capable in that they can be configured for Profinet, Ethernet/IP and Modbus TCP with our free software tool MultiFieldbus Configuration Tool (MFCT). Both IP20 and IP65/67/69K-based master modules are offered for the customer to choose based on the application. The devices can be configured with ease with our free software S7-PCT tool. The tool can be standalone or be integrated in our software platform for automation, TIA Portal. Mapping of data from the devices can be done efficiently by the user data type created by the S7-PCT tool and using the UDT in TIA Portal to create a custom tag with all the real-time data from the device. Function calls are provided for reading and writing other parameter data to and from the device.
About the Author
Mike Bacidore
Editor in Chief
Mike Bacidore is chief editor of Control Design and has been an integral part of the Endeavor Business Media editorial team since 2007. Previously, he was editorial director at Hughes Communications and a portfolio manager of the human resources and labor law areas at Wolters Kluwer. Bacidore holds a BA from the University of Illinois and an MBA from Lake Forest Graduate School of Management. He is an award-winning columnist, earning multiple regional and national awards from the American Society of Business Publication Editors. He may be reached at [email protected]